Urinary incontinence happens when the bladder becomes weak and urination happens by accident. Although they seldom want to talk about it, urinary incontinence affects women twice as often as men. The cause may be related to childbirth or menopause, and the structure of the female urinary tract plays a role as well.
If you suffer from this problem, it’s important to realize you are not alone. More than 33 million Americans deal with urinary incontinence or a bladder condition. Unwanted urinary activity occurs in both men and women and increasing age can be a partial cause. Is is estimated that one out of three women in the United States has a bladder problem.
 Bladder control problems can vary, from occasional urine leakage that happens when you cough or sneeze, to having sudden urges to urinate so strong you do not make it to the toilet in time. There are several basic forms of incontinence and you can have more than one condition. There is urge incontinence, where you will feel a need to urinate all of a sudden as the bladder involuntarily contracts, compelling you to urinate immediately. Another form is stress incontinence. This is caused when physical stress from coughing or sneezing, or athletic activity, puts pressure on the bladder and causes leakage.
Bladder control problems can vary, from occasional urine leakage that happens when you cough or sneeze, to having sudden urges to urinate so strong you do not make it to the toilet in time. There are several basic forms of incontinence and you can have more than one condition. There is urge incontinence, where you will feel a need to urinate all of a sudden as the bladder involuntarily contracts, compelling you to urinate immediately. Another form is stress incontinence. This is caused when physical stress from coughing or sneezing, or athletic activity, puts pressure on the bladder and causes leakage.
Some women experience overflow incontinence, which happens when you leak urine because your bladder does not empty all the way.
Assessing Causes of Urinary Leakage
When you make an appointment, your doctor or a physician assistant will ask for a thorough history of the problem, followed by a physical exam. Some simple and painless tests may be taken. Urinalysis is a test in which a urine sample is checked for traces of blood, signs of infection, nitrates, or other indications of a medical problem. You may be asked to create a bladder diary, keeping a record for a few days to track the amount of fluids you drink and the frequency and amount of urine, as well as details of urgency or leakage.
Another test may be a post-void residual measurement. You will urinate into a container, and then your doctor uses ultrasound to measure the amount of urine left in your bladder.
Treating Bladder Control Problems
- Changing your diet and performing Kegel exercises may help with both urge and stress incontinence. Additional treatments may be recommended ranging from medications to surgery.
- Medications can be prescribed, including anticholinergics (used to block neurotransmitters), antidepressants, estrogens, or nerve-stimulating drugs.
- Injection therapy involves the injection of collagen and other compounds to bulk up the urethra.
- Botox injection is another possibility. Injecting Botox into the bladder partially paralyzes muscles to help reduce overactivity.
- Surgical options are available for treating bladder control issues. They include urethral slings or mesh tape inserted to support a sagging urethra, or sacral nerve stimulation through an implanted device that calms nerves of the bladder.
It is best to make an appointment with a urologist if you are experiencing bladder control problems. Our doctors at Advanced Urology Institute have years of experience with treating bladder problems and working with patients to find the best solutions. For more information, visit the Advanced Urology Institute website.





 Certified physician assistants go through a rigorous graduate-level training program that takes more than two years to complete. The degree program must be accredited by both the Committee on Allied Health, Education and Accreditation, and the Accreditation Review Commission on Education for the Physician Assistant. After successful completion of the academic portions, the graduates must pass the national Physician Assistant National Certifying Exam. The final stages include formal application with the Florida Board of Medicine and completion of 2,000 hours (about one year) of supervised clinical practice.
Certified physician assistants go through a rigorous graduate-level training program that takes more than two years to complete. The degree program must be accredited by both the Committee on Allied Health, Education and Accreditation, and the Accreditation Review Commission on Education for the Physician Assistant. After successful completion of the academic portions, the graduates must pass the national Physician Assistant National Certifying Exam. The final stages include formal application with the Florida Board of Medicine and completion of 2,000 hours (about one year) of supervised clinical practice.
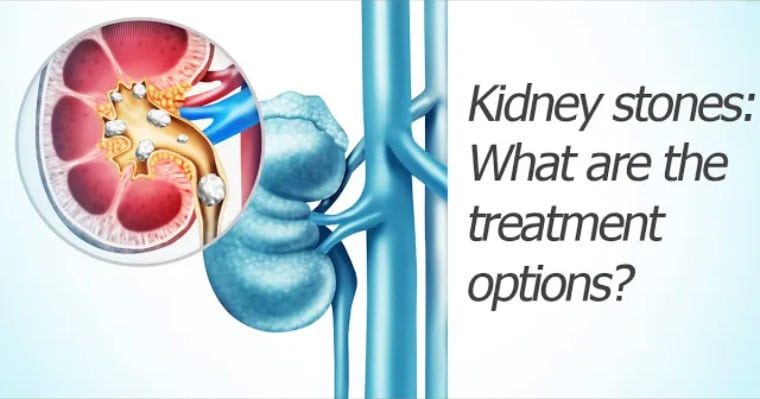
 entities formed of different types of crystals. When they become large, they are extremely painful. They are called
entities formed of different types of crystals. When they become large, they are extremely painful. They are called