Advanced Urology Institute is a leading urology practice that excels in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the female and male urinary tracts and problems of the male reproductive system. Designed to be a world-class urology center, AUI brings together a huge group of doctors who are specialists in various areas to offer coordinated, effective and top-notch urology services to their patients. From restoring fertility to curing cancer, addressing incontinence to treating kidney stones, the urology services offered by AUI touch every sphere of life and bring back smiles to the faces of all who come to us for help.
Satisfying patient experience
By centralizing the administration of urology services, the doctors are able to concentrate on delivering the highest quality service to patients from initial consultation to follow-up care. The unique partnership and collaboration of many doctors and several care centers ensures that every physician or center in AUI can broaden the scope of expertise and services provided to patients, resulting in a positive experience to meet the unique needs of our patients wherever they are. At Advanced Urology Institute, we invest our time and effort, skills and experiences to make our services better. We are dedicated to delivering life-saving medical and surgical urology care in a prompt, safe and affordable manner. For us, it is not merely our job. The wellbeing and health of our patients is our number one priority.
Innovative and cutting-edge techniques
Advanced Urology Institute is a pool of urologists from multiple subspecialties. We pride ourselves on expertise and ensure that all members of our team continue to undertake training in the latest specialized surgical and medical techniques. Our experienced urologists work collaboratively to deliver highly complex treatment and care individualized to the needs of our patients. And with our exceptional range of specialist urologists, we are able to deliver more complex and innovative surgical services not available anywhere else. As a group, we are able to pool our resources, enabling all our members to have access to better equipment, instruments and tools for managing urologic disorders. Each member of the team has more experts to seek help from and we frequently send patients to other colleagues among us with more expertise and experience. As a result, we do as good a job and deliver as great results as any other premier urology centers in the country.
Unparalleled range of services
At Advanced Urology Institute, we offer a broad range of life-improving, life-extending and life-saving services to patients of all ages. Those who come to AUI have access to every possible treatment option available. In fact, most of the patients we see usually come with issues that other institutions are not able to diagnose or treat. As a team, we are committed to delivering the right care to every patient the first time they come, guaranteeing the highest rate of treatment success. We also endeavor to provide individualized, comprehensive care for all urologic conditions and diseases, giving every patient the opportunity to tap into our collaborative and team approach to have their issues resolved. At AUI, we ensure that all our hospitals, clinics, health care facilities and physicians serve with integrity and unwavering commitment to excellence. We listen to every concern, tailor every evaluation, apply the right treatment and do what is best for the patient. As a team, we deliver beyond the expectations of our clients.
For more information, visit the “Advanced Urology Institute” site.



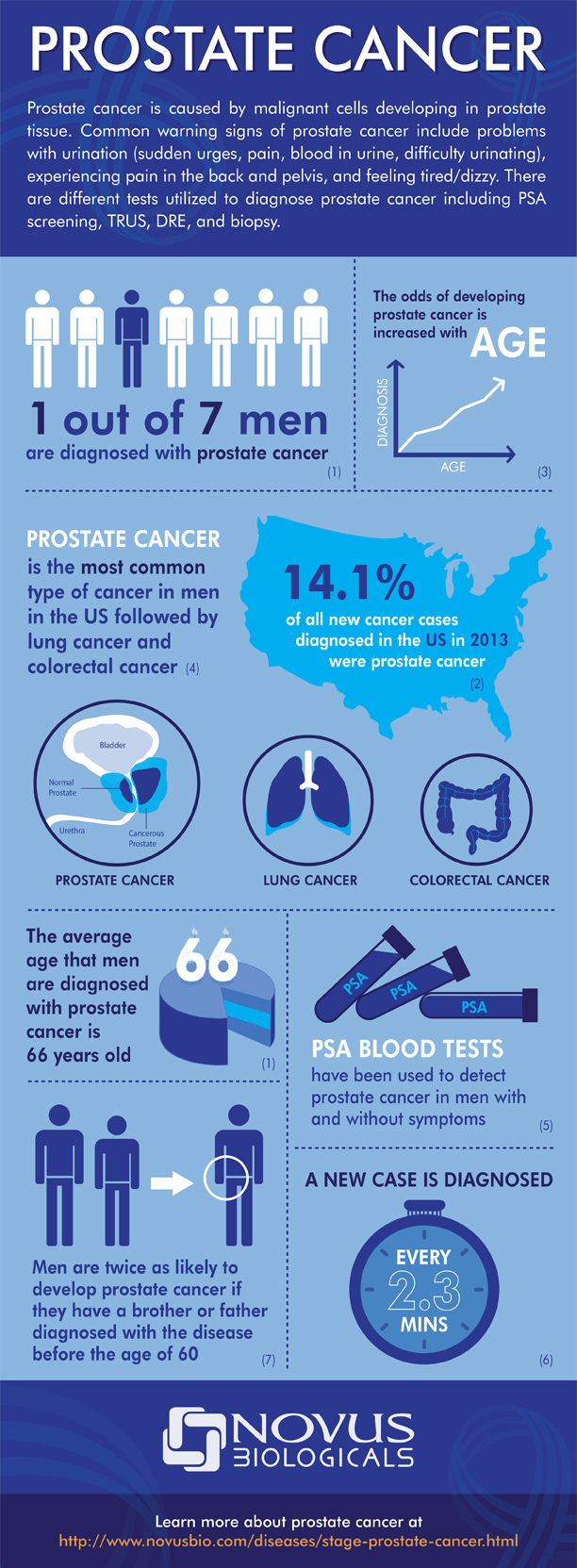
 The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test measures the amount of the protein (PSA) released in blood by prostate cells. Even though both normal and cancerous (abnormal) prostate cells produce the protein, higher blood levels of PSA indicate the possibility of cancer. The PSA test is one of the best indicators of prostate cancer and is recommended by urologists because it is widely available, relatively inexpensive and is a low-risk blood test for patients.
The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test measures the amount of the protein (PSA) released in blood by prostate cells. Even though both normal and cancerous (abnormal) prostate cells produce the protein, higher blood levels of PSA indicate the possibility of cancer. The PSA test is one of the best indicators of prostate cancer and is recommended by urologists because it is widely available, relatively inexpensive and is a low-risk blood test for patients. There are many causes of kidney stones, such as dehydration, excessively acidic urine,
There are many causes of kidney stones, such as dehydration, excessively acidic urine,  Apple cider vinegar
Apple cider vinegar Kidney beans not only resemble the kidneys but also remove waste and toxins from the kidney and flush out kidney stones effectively. Kidney beans are rich in Vitamin B, fiber and several minerals which help to clean the kidney and boost the function of the urinary tract.
Kidney beans not only resemble the kidneys but also remove waste and toxins from the kidney and flush out kidney stones effectively. Kidney beans are rich in Vitamin B, fiber and several minerals which help to clean the kidney and boost the function of the urinary tract. Lemon juice is naturally acidic and increases
Lemon juice is naturally acidic and increases  Watermelon is a mild diuretic. It hydrates and cleanses the kidneys. It is also rich in lycopene, which improves cardiovascular health and ensures well-functioning kidneys. Watermelon also has large quantities of potassium salts which regulate acidity of urine and prevents stone formation. In fact, eating watermelon regularly is great for kidney health.
Watermelon is a mild diuretic. It hydrates and cleanses the kidneys. It is also rich in lycopene, which improves cardiovascular health and ensures well-functioning kidneys. Watermelon also has large quantities of potassium salts which regulate acidity of urine and prevents stone formation. In fact, eating watermelon regularly is great for kidney health. Both the juice and seeds of pomegranate contain large amounts of potassium and therefore are effective in removing kidney stones. Potassium lowers acidity of urine, prevents stone formation because of its astringent properties, curtails crystallization of minerals, and flushes out toxins and waste from the kidneys.
Both the juice and seeds of pomegranate contain large amounts of potassium and therefore are effective in removing kidney stones. Potassium lowers acidity of urine, prevents stone formation because of its astringent properties, curtails crystallization of minerals, and flushes out toxins and waste from the kidneys. Basil is an effective diuretic. It removes kidney stones and improves kidney functioning. Basil also lowers the level of uric acid in blood and improves kidney health. Its ingredients such as essential oils and acetic acid break down kidney stones and allow for smooth removal. Basil is also a pain killer.
Basil is an effective diuretic. It removes kidney stones and improves kidney functioning. Basil also lowers the level of uric acid in blood and improves kidney health. Its ingredients such as essential oils and acetic acid break down kidney stones and allow for smooth removal. Basil is also a pain killer. When dates are soaked in water for 24 hours and then consumed after seeds are removed, they are effective in dissolving and flushing out kidney stones. Dates are rich in fiber, helping to reduce the risk of kidney stones. The magnesium ingredient in dates also cleanses the kidneys.
When dates are soaked in water for 24 hours and then consumed after seeds are removed, they are effective in dissolving and flushing out kidney stones. Dates are rich in fiber, helping to reduce the risk of kidney stones. The magnesium ingredient in dates also cleanses the kidneys. Consuming tea made using dried organic dandelion or fresh
Consuming tea made using dried organic dandelion or fresh