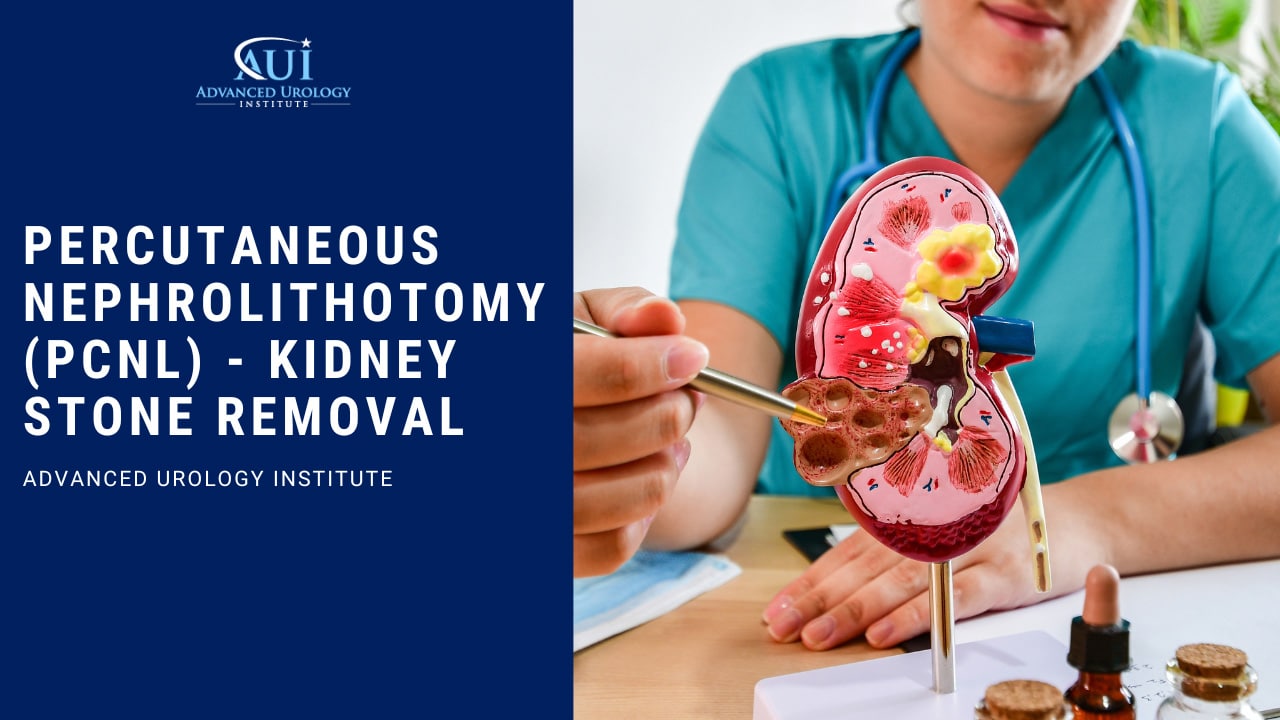
Advancements in urology now lead to better treatment solutions for kidney stones such as precutaneous nephrolithotomy or PCNL.
Continue readingExploring Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction
Explore treatment options for erectile dysfunction with the expertise of the urologists at Advanced Urology Institute in Florida.
Continue readingHealthcare in Florida: The Profound Impact of a Career in Urology
Explore the inspiring journeys of Drs. Selinger and Ramos, showcasing the profound impact of a dedicated career in urology.
Continue readingVasectomy: A Quick and Easy Birth Control
A vasectomy can be done in two ways:
1. No scalpel Vasectomy. In this procedure, a urologist feels the scrotum and finds the vas deferens. Once the vas deferens can be felt, a clamp is placed on it to hold it in place. A hole is made in the skin and the vas deferens is lifted out. It is cut and the separate ends are tied and put back into place.
2. Conventional Vasectomy. Small incisions are made on each side of the scrotum. The vas deferens is then cut and a small piece of it may be taken out. The separate ends are then tied or seared. This procedure often requires the use of an anesthetic.
The procedure takes about thirty minutes. The outcome, however, takes a while to be realized. Most professionals advise that it takes about three months, or at least 15-20 ejaculations, for semen to become completely sperm free. Before then, it may be advisable to use other forms of birth control. Aftercare usually requires mild pain medication and wearing supportive underwear. Ice packs also can help with the pain. Most men recover within one week.
What to consider before undergoing a Vasectomy
The high success rate of a vasectomy requires absolute certainty on the part of the man that he does not wish to have any more children. In instances in which the man is married, it is necessary for him to discuss the matter with his spouse. A vasectomy is widely considered to be irreversible. When it is reversible, the procedure is sensitive and difficult.
The importance of having the advice of a urologist before, during and after the procedure cannot be understated. Qualified urologists can be found in most hospitals and the search for one can be undertaken online. The Advanced Urology Institute runs a site with very relevant information and this can be a good place to start. For more information on vasectomy, visit the “Advanced Urology Institute” site.
What Are The Advantages of Using Robots in Surgery?
The use of robots in surgery, also called robotic surgery or da Vinci surgery, is an impressive fusion of medicine and engineering that has transformed the medical field. It involves the use of miniaturized robotic instruments inserted into the body through a small incision and guided through the operation by a surgeon sitting at a console. It has brought the following advantages:
1. Increased visibility and precision
The surgeon views the entire anatomy, with specific focus on the surgical site, through a 3D high definition camera. This means even the smallest blood vessels are visible and the surgeon can follow the movement of the instruments with pinpoint accuracy. The surgeon has a clear view of what they are working on and the incidence of human error is cut down dramatically. The smaller instruments also can access tight spots that otherwise would be impossible or extremely difficult for a surgeon to reach.
2. It is a minimally invasive procedure
The incisions made in robotic surgery are only done to accommodate the tiny instruments. There is a world of difference between this procedure and open surgery where a surgeon has to make large incisions on skin and sometimes even cut through muscle to reach the surgical site. The minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery means numerous additional benefits, such as:
a. It causes only a little bleeding;
b. It results in minimal scarring;
c. The patient requires a short recovery period;
d. The patient suffers less pain and physical discomfort, both during and e. after the surgery;
f. There is a very small chance of post-surgery infections;
g. Overall there is less surgical trauma; and
h. There is a rapid return to normal everyday activities.
3. It is less strenuous on surgeons
Most surgeries take two to three hours but complex procedures go on for longer. Surgeons must stay sharp and focused, and in the case of open surgeries, on their feet for as long as the surgery takes. It is only fair to expect that they might suffer from fatigue. In robotic surgery, the surgeon sits can view the anatomy of the patient and control the surgical instruments while sitting at a console. This is definitely easier on the surgeon, who should be able to better maintain better concentration during long surgeries. It also makes it less likely for a mistake to occur.
Robotic surgery is available for almost all surgical procedures. A patient should see a specialist to discuss the applicability of robotic surgery to his or her case. For prostate, kidney and other urinary system problems for instance, the highly specialized urologists and doctors at Advanced Urology Institute can help you with a diagnosis as well as explain the best procedures for you, including robotic surgery. For more information about robotic surgery, visit the “Advanced Urology Institute” site.
What Treatments Are Available For ED?
Erectile dysfunction is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse. It is not incidental to aging, though in reality it occurs mostly in men over the age of 40. The causes of erectile dysfunction are varied, and the first step is to establish whether it is caused by an underlying condition. Whatever the cause, however, there are various options when it comes to the treatment of erectile dysfunction.
1. Oral Medication (Pills)
Like many other medical conditions, erectile dysfunction can be treated effectively by taking medicine. Oral medicines for erectile dysfunction fall under a group called phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE 5) inhibitors. They work by preventing the functioning of the enzyme phosphodiesterase type 5 whose job is to control blood flow to the penile arteries. When the enzyme is not functioning, blood vessels relax, allowing blood to reach the penis, therefore causing an erection. The most common PDE 5 inhibitors are:
a. Sildenafil- commonly referred to as Viagra
b. Avanafil – also known as Stendra
c. Tadalafil – also known as Ciaris; and
d. Varednafil- also known as Levitra
Most of these medications are widely available. It is necessary, however, to consult with a urologist before taking any of them. A trained urologist should be able to assess a patient’s condition and advise whether oral medication is likely to work and if so, which of the available medicines is best suited to the patient’s case.
2. Penile implants
For some men, especially those with underlying conditions, oral medication does not work. They may have to resort to other treatment options and the most common of these is the penile implant. This involves a minor surgical procedure and the placing of an implant that causes an erection. There are two choices when it comes to the implant. There is the inflatable implant and the malleable/ semi-rigid implant. Both options have their advantages and disadvantages and the patient will decide based on his circumstances. Overall, however, both implant options report a success rate of over 90 percent.
3. Vascular reconstructive surgery.
Vascular reconstructive surgery involves reconstructing the arteries within the penis to increase blood flow. This last option is neither common nor popular. It is a very difficult, and therefore expensive, procedure. Additionally, it is not always successful and a patient might face the risk of relapse.
It is possible to treat erectile dysfunction. But the right treatment option must be sought for each individual case. It is recommended that anyone experiencing erectile dysfunction should see a urologist. The highly qualified and experienced urologists at Advanced Urology Institute can provide consultation, technology and treatment plans to help patients with erectile dysfunction. Want to find out more about erectile dysfunction? Visit the “Advanced Urology Institute” site.
Radical Prostatectomy vs Radiation Therapy
Introduction
Radical prostatectomy and radiation therapy are both cancer treatment methods. Radical prostatectomy is specific to prostate cancer and involves the surgical removal of the prostate, either alone or with other surrounding tissues such as the seminal vesicles and some lymph nodes. There are currently various ways in which a radical prostatectomy can be carried out, including robot assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy, open prostatectomy and laparoscopic prostatectomy.
On the other hand, radiation therapy, also known as radiotherapy, is used in the treatment of almost all cancers, including prostate cancer. It involves the use of high doses of radiation to kill cancer cells or to slow their development by destroying their DNA. For radiation therapy to work effectively, it needs to be applied consistently over a period of time.
Choosing between Radical Prostatectomy and Radiation Therapy
The main advantage of radical prostatectomy is that it is arguably a one time procedure. It takes just a few hours to completely remove the affected prostate and the patient is likely to recover fully, albeit gradually and with the monitoring of a urologist. The main disadvantage is that it is appropriate only where the cancer has not spread to other organs outside the prostate. If it has spread, then removing the prostate and leaving behind other affected organs will have no effect at all. In cases where the cancer has spread, radiation therapy may be the more reasonable choice.
Other factors that urologists and surgeons consider before suggesting either procedure include:
1. Age of the patient — Radical prostatectomy is offered mostly to men under 70 years of age because they are more likely to live longer and be able to survive any long term effects of the disease.
2. The natural progression of the disease — Slow progression of a non-aggressive tumor does not lend itself to surgery. This is a case that can be managed by what is called watchful waiting where the disease is monitored constantly but treatment is deferred for a while.
3. The possibility of cure — The goal of radical prostatectomy is to cure the patient of prostate cancer. If for whatever reason it appears that it is unlikely that this objective will be achieved, then radiation therapy or other forms of treatment should be preferred.
Conclusion
It is important to choose the treatment option that works for your body. In order to make the right choice, make a point of consulting a qualified urologist. Reading material on the subject should also be helpful, and sites such as the one operated by the Advanced Urology Institute should be a good place to start.
For more information, visit the Advanced Urology Institute website.
Bay Regional Cancer Center Closing Down
 We regret to inform you that due to Hurricane Michael, we are no longer providing Radiation Treatment and forced to close our facility at Bay Regional Cancer Center.
We regret to inform you that due to Hurricane Michael, we are no longer providing Radiation Treatment and forced to close our facility at Bay Regional Cancer Center.
Your health and well-being are of utmost importance to the staff at Advanced Urology Institute/Bay Regional Cancer Center. Dr.Steven Finkelstein is still in our community and is currently practicing at Florida Cancer Affiliates North Florida. If you wish to keep him as a provider, please call his new office staff at (850) 763-0036. If you do not wish to continue your care with Dr.Finkelstein, we encourage you to choose another provider as soon as possible to ensure timely care for your medical needs.
Your medical records are confidential and will remain on file with Advanced Urology Institute. A copy of your records can be released to you or your new provider with your written permission. Please note, by law we cannot share your medical information without your written consent. You may sign this form at our office located at 80 Doctors Drive Panama City, FL 32405 or give us a call at (850) 785-8557.
Please be assured that my staff and I will do everything we can to make the transition smooth and stress free. Thank you for trusting Dr.Finkelstein and our wonderful staff with your healthcare needs. It has been a pleasure to provide your care, and we wish you the best in the future.
Miriam Williams
Chief Administrative Officer
What is MRI with Transrectal Ultrasound Fusion-Guided Prostate Biopsy
 Prostate cancer has a new standard of care in MRI-guided fusion biopsy with transrectal ultrasound. While a prostate biopsy has been the only way to get a definitive diagnosis of prostate cancer, it has only been working if cancer cells are identified in the sample tissue. But in some cases, such as when the tumor occurs at the top surface of the prostate or other unusual locations, a biopsy may not give a correct diagnosis. For instance, the standard TRUS (transrectal ultrasound) guided biopsy in which tissue samples are collected from the prostate in a systematic pattern gives a negative result with tumors located in unusual areas of the prostate. About 15-20 percent of tumor locations can be missed by the biopsy needle.
Prostate cancer has a new standard of care in MRI-guided fusion biopsy with transrectal ultrasound. While a prostate biopsy has been the only way to get a definitive diagnosis of prostate cancer, it has only been working if cancer cells are identified in the sample tissue. But in some cases, such as when the tumor occurs at the top surface of the prostate or other unusual locations, a biopsy may not give a correct diagnosis. For instance, the standard TRUS (transrectal ultrasound) guided biopsy in which tissue samples are collected from the prostate in a systematic pattern gives a negative result with tumors located in unusual areas of the prostate. About 15-20 percent of tumor locations can be missed by the biopsy needle.
What makes the MRI-ultrasound fusion biopsy more definitive?
The MRI-ultrasound fusion approach is an improvement on the traditional 12-core TRUS, which involved taking biopsies from twelve prostate areas where the cancer is considered more likely to occur. With the TRUS biopsy, about 70 percent of men who have a negative biopsy result are not essentially free of the cancer. The MRI-ultrasound fusion technology blends the superior imaging capability of the high-definition multi-parametric (mp) MRI with real-time ultrasound imaging. There is better visualization of the suspicious areas of the prostate where the cancer may occur that may not be visible on ultrasound alone. The fusion-guided biopsy detects almost twice as many prostate cancers in all stages as the standard TRUS biopsy.
The ability of MRI-ultrasound fusion-guided biopsy to create a three-dimensional (3D) map of the prostate ensures that doctors are able to see the targeted areas of the prostate better and perform more precise biopsies. The technology uses a machine known as UroNav developed by Invivo, which is supplied with sophisticated software to produce super-detailed MRI images and fuse them with the ultrasound images generated by a transrectal probe administered on the patient in an outpatient setting. The resulting images enable the examining physician to direct biopsy needles with pinpoint accuracy and to easily access any lesions or suspicious areas revealed by MRI. The technology allows the urologist to hit the target spot more accurately and improves cancer detection rate. In fact, it is primarily used for men who have an ongoing suspicion of prostate cancer, such as those with consistently elevated PSA, but whose TRUS biopsy results are repeatedly negative.
Fewer biopsies, more accurate detection
The fusion-guided biopsy is a very targeted approach in which biopsies are performed only in highly suspicious areas of the prostate appearing in the MRI image. As a result, significantly fewer biopsies are done with the MRI-ultrasound fusion than with the traditional TRUS technique, minimizing the adverse effects that often accompany repeat biopsies. Multiple prostate biopsies can lead to complications such as bleeding, infection, urinary retention problems, sepsis or even death.
In spite of fewer biopsies, the MRI fusion approach increases the rate of detection of aggressive prostate cancer. The extensive MRI images obtained before the biopsy helps highlight both high-risk and intermediate-risk cancers often missed by traditional TRUS biopsy. With MRI-ultrasound fusion, the likelihood of detecting cancer increases as the grade of the tumor increases. The use of MRI fusion biopsy helps to avoid metastatic disease by finding cancer before it spreads to other areas of the body.
Improved cancer differentiation
Through MRI fusion, doctors are able to more accurately differentiate cancers that require treatment from the ones that should undergo watchful waiting (active surveillance). Fusion technology is able to show higher-risk cancers and does not highlight the insignificant low-grade tumors, making it less likely for urologic oncologists to over-treat indolent and low-grade cancers. A number of prostate cancers are low-grade, non-aggressive and do not cause problems at all and treating them through chemotherapy, radiotherapy or surgery can impair the quality of life or even cause death. MRI fusion effectively saves patients from the adverse effects of treating low-grade tumors. Fusion technology eliminates up to 50 percent of prostate cancer treatments that are unnecessarily administered on low-grade cancers.
At Advanced Urology Institute, we have adopted the MRI-ultrasound fusion biopsy and changed the way we screen, evaluate and diagnose prostate cancer. It has become our standard for detecting prostate cancer and we believe in the next few years it will be the gold standard for detecting the cancer. We are proud that it offers a higher detection rate, superior accuracy and reduces the rate of repeat biopsies — making our practice one of the best places for detection and monitoring of the cancer. It helps us deliver the best treatment outcomes for our patients.
If you think you are at high risk of prostate cancer or already have started experiencing some symptoms, let us show you how the precision of our high-definition MRI fusion machine, the expertise of our skilled physicians in MRI fusion biopsy and the know-how of our radiologists proficient in multi-parametric MRI imaging can help you. For more information on the treatment and diagnosis of prostate cancer, visit the “Advanced Urology Institute” site.
TO OUR PATIENTS AFFECTED BY HURRICANE MICHAEL IN THE PANAMA CITY AREA

Our thoughts and prayers to our patients affected by Hurricane Michael in the Panama City Area. Our Panama City Location is currently open from 8AM to 3PM Mon-Fri until further notice. Our phone number is 850-785-8557.
For access to more information and resources please see this announcement from former AUI urologist Rep Neal Dunn: Click Here
What Does the Prostate Gland Do?
The prostate, found only in men, is a tiny, walnut-sized muscular gland in front of the rectum and just below the bladder. It surrounds the urethra, which transports urine to the penis from the bladder, and is essential for the normal functioning of the male genitourinary system. The prostate makes prostatic fluid, which forms a substantial portion of semen. During ejaculation the prostate contracts and closes off the opening between the urethra and bladder, ensuring that prostatic fluid squirts into the urethra and semen is pushed out at speed.
So what does the prostate do?
The prostate is not an essential organ for life, but it’s quite crucial for reproduction. It plays an active part in reproduction by secreting the prostatic fluid, which forms part of healthy semen — the perfect environment for the transit and survival of sperm. Healthy semen includes the enzyme PSA (often measured during screening for prostate cancer), together with other substances secreted in the prostate and seminal vesicles, such as citrate, zinc and fructose, which supply sperm with the energy to travel to the egg. There are also various antibodies in semen to protect sperm and the urinary tract from bacteria and different pathogens.
What are the constituents of prostatic fluid?
The prostate secretes a milky fluid, the prostatic fluid, which makes up about 30 percent of the total fluid that’s ejaculated. The prostatic fluid contains various ingredients, such as enzymes, citric acid and zinc, which keeps sperm alive and protects them and the genetic codes they carry. PSA (prostate-specific antigen) is one of the enzymes in the fluid that, after ejaculation, makes semen runnier and helps sperm travel through semen more easily, which increases the likelihood of successful fertilization of an egg. While prostatic fluid is weakly acidic, the other constituents of semen turn it alkaline overall, which helps to counteract vaginal acidity and prevent damage of sperm.
Growth of the prostate
The prostate grows bigger as men age. Typically the prostate undergoes growth during adolescence driven by the male hormone, testosterone, and the hormone’s byproduct, dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Testosterone hormone is primarily produced in the testes, but smaller quantities also can be secreted in the adrenal glands found just above the kidneys. By the age of 40 the prostate might have grown from a walnut-sized to apricot-sized gland. And by the age of 60 it might have reached the size of a lemon.
Benign prostatic enlargement (BPH)
While the prostate is strategically located to deliver the prostatic fluid and squeeze things along during ejaculation, its position around the urethra makes it a liability when it grows or gets bigger. A swollen prostate will compress the urethra and irritate the walls of the bladder, resulting in interference with normal urine flow. In fact, over 50 percent of all men in their 60s have symptoms of prostate enlargement, a condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). And by the age of 70 to 80, a man’s risk of BPH increases to 90 percent, with symptoms such as leaking or dribbling urine, frequent urination, weak or stuttered urine stream.
While the size of your prostate will not always influence how severe the obstruction or symptoms are, BPH can cause serious complications over time, such as urinary tract infections, bladder damage, kidney damage, incontinence and bladder stones, due to bladder strain and urinary retention. So it’s important to see a urologist as soon as you have urinary issues so BPH can be detected early and treated.
Prostate cancer
Another health problem associated with the prostate is prostate cancer, which is the most frequent cancer in men. It occurs in 1 out of 7 men over their lifetime, and more than 200,000 men are diagnosed with the cancer annually. Prostate cancer is frequent in men age 50 and older, but the largest number of cases is found in men 70 to 80 years old. About 3.8 percent of men diagnosed with the cancer die of the disease, while 7 in 10 newly diagnosed patients currently survive past 5 years. As doctors, our role is to screen for the cancer, detect aggressive forms early and prevent any problems that may occur due to obstruction.
So what’s your role?
Tell your doctor about your urinary problems as soon as possible. The symptoms may not only suggest BPH, but also may indicate a more serious condition. With a prompt visit to the doctor, a more serious condition such as prostate cancer can be ruled out.
Want to know more about BPH, prostate cancer and other urological problems? Visit the “Advanced Urology Institute” site.
4 Effective Ways to Treat Kidney Stones
Dreading the agony and pain of kidney stones? You don’t have to because the condition is treatable. And the pain and discomfort disappears as soon as the stones are removed.
The treatment you get depends on the type, size and cause of the stones and on the severity of your symptoms. For instance, if you are having very severe pain, your urologist will give you an injection to relieve the pain. A second injection may be given after 30 minutes if you are still in deep pain. You also may be injected with anti-emetic medication to relieve vomiting and nausea.
Apart from dealing with the symptoms of the kidney stone, your doctor will administer treatment to remove the stone. The 4 effective ways to remove kidney stones include:
1. Spontaneous Passage
If your kidney stones are small (less than 4 mm diameter) and you have minimal symptoms, you won’t require invasive treatment. In fact, once your urologist assesses that you can tolerate the stone, you will be given time so the stone can pass out on its own. In such a case, the urologist will only make the following recommendations:
- Drrink a lot of water, as much as 1.9-2.3 liters a day, to help you flush out the stone from your urinary tract. In this case, you have to drink enough fluid — until your urine is colorless. So if your urine is still brown or yellow after drinking water, then you know that you aren’t drinking enough fluid.
- Use pain relievers as you wait for the stone to pass out spontaneously. Since even a very small kidney stone can be really painful, your urologist may recommend pain relievers such as acetaminophen (Tylenol or others), naproxen sodium (Aleve), or ibuprofen (Motrin IB, Advil or others) to relieve the pain. The pain will only last a few days and often disappears soon after the stone is passed.
- Take medication to help you pass the stone. Such medication, often alpha blockers, help to relax ureter muscles and allow the stone to be flushed out of your urinary system faster and with less pain.
With these recommendations you are expected to wait until the stone passes out and then to collect the stone for analysis by your urologist in order to help determine if there is need for further treatment. To collect the stone, you simply filter your urine through a stocking or gauze as you urinate.
2. Extracorporeal Shock-Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL)
What if your kidney stone is too large to pass out in urine? In that case, your doctor may recommend a procedure called extracorporeal shock-wave lithotripsy. The ESWL procedure uses sound waves to generate strong vibrations (called shock waves), which break the stone into tinier pieces that can easily and less painfully pass through urine.
The high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) are directed at the stone from a machine for 45-60 minutes. Because this can be a bit uncomfortable, you will undergo the procedure under light anesthesia or sedation to reduce the discomfort. The ESWL procedure is 99 percent effective for kidney stones that are up to 20 mm (0.8inch) in diameter. But you may require one or more ESWL sessions for the kidney stones to be effectively removed.
3. Ureteroscopy
What if the stone is stuck somewhere in your urinary tract, such as the ureter? In that case, your urologist may recommend ureteroscopy, a procedure that’s also called RIRS (retrograde intrarenal surgery). During ureteroscopy your doctor passes a long thin telescope, a ureteroscope, through your urethra, into the bladder and into the ureter, or wherever the stone is stuck.
After locating the stone the urologist uses a special instrument or laser energy to break the stone into tiny pieces that can pass out naturally in urine. The doctor then may place a small plastic tube (stent) temporarily in the ureter to help drain the stone fragments into your bladder, relieve swelling and hasten healing. Ureteroscopy is conducted under general anesthesia, so you shouldn’t operate machinery or drive for up to 48 hours after treatment. It is 50-80 percent effective for kidney stones that are 15 mm (0.6inch) in diameter.
4. Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
In circumstances where ESWL isn’t appropriate, such as when you are obese, larger stones may require an alternative procedure called percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL). It is a surgical procedure for removing kidney stones using a small thin telescopic instrument known as a nephroscope. The instrument is inserted through a small incision made in your back and guided carefully to your kidney or ureter. Once the stone is located it is either broken into smaller pieces (with pneumatic energy or laser) or pulled out. PCNL has 86 percent efficacy for kidney stones of 21-30 mm in diameter and is performed under general anesthesia.
When should you seek treatment for kidney stones? You need urgent treatment if:
- Your pain is sudden, severe or gets worse.
- You have a fever of 100.4 F or higher.
- You have one or more episodes of shaking or shivering.
At Advanced Urology Institute we have assembled a team of skilled and experienced urologists to help diagnose and treat kidney stones and other urological problems safely and effectively. We offer all 4 effective treatments for kidney stones and have the latest equipment and technology to make the treatment process as painless and comfortable as possible. So don’t try to endure the pain even a day longer before you see us and let us fix it. For more information on kidney stones and other urological disorders, visit the “Advanced Urology Institute’” site.
Benefits of Testosterone Therapy
Secreted primarily in the testicles, testosterone is a critical hormone responsible for male growth and masculine characteristics. The levels of testosterone increase exponentially in childhood and hit a peak during adolescence, then begin to decline by about 1 percent every year between the ages of 30 and 40 years and older. The gradual decline can be due to either normal aging processes or a condition called hypogonadism. Hypogonadism is a disorder in which the body fails to produce normal quantities of testosterone. It often occurs when there is a problem with the pituitary gland (which controls the testicles) or with the testicles themselves. For men with testosterone levels below the normal range, testosterone replacement therapy can relieve symptoms of low-T and provide many benefits.
Normal Testosterone Levels
For men, the normal range of total testosterone is 300-1,200 ng/dL (nanograms per deciliter). Men with testosterone levels within this range rarely have any problems associated with low testosterone. However, since total testosterone does not usually provide the full picture, doctors often measure and use the levels of free testosterone to assess a man’s vulnerability to low-T symptoms. Free testosterone means the amount of testosterone hormone that is active in the body at any given time. Men with total testosterone levels within the normal range can still suffer from the classic low-T symptoms if their free testosterone levels fall short.
Implications of Low Free Testosterone
The free testosterone level is a clearer indicator of a man’s true testosterone status. In fact, low free-T is almost exclusively associated with sex difficulties. Low testosterone diminishes sex drive in men and results in loss of energy and motivation and poor performance in bed. Men with low testosterone also may suffer from fewer spontaneous erections, slightly lower sperm count, increased body fat, decreased muscle strength and mass, fragile bones, tenderness or swelling of breast tissue, hot flashes, increased fatigue, feelings of depression and sadness, trouble with concentration and memory, lowered self-confidence and motivation, and a degraded overall sense of well-being. These symptoms can be relieved through testosterone replacement therapy.
Benefits of Testosterone Replacement Therapy
There is no doubt that testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can quickly revive a man’s interest in sex, boost his ability to maintain an erection and recreate the “wow” factor of his orgasms. Treating sexual symptoms is a good enough reason for men to start testosterone therapy. But because testosterone therapy also can improve a man’s health beyond the bedroom, bringing testosterone levels back to normal is a good decision for every man who wants to feel better. Replacement therapy improves bone mineral density, boosts overall bone strength, increases muscle mass and strength, boosts red blood cell production, enhances hemoglobin levels and corrects both iron deficiency anemia and unexplained anemia. Testosterone therapy also improves mood, alleviates depression, irritability and fatigue, relieves disorders linked to testosterone deficiency such as osteoporosis and boosts insulin sensitivity, which can benefit men with diabetes or minimize the risk of diabetes in men with functioning pancreas.
Should You Opt For Testosterone Therapy?
Testosterone replacement therapy is ideal for men with testosterone levels below 300 ng/dL or those experiencing symptoms of low testosterone. Undergoing replacement therapy can help you restore your testosterone levels to normal and improve your libido, cognition, mood, bone density, muscle mass and red blood cell production. However, you should remember that the therapy is only necessary if you have low T. If you are not sure whether the therapy is right for you, speak with your doctor. The doctor will conduct the requisite tests for low-T and guide you accordingly.
At Advanced Urology Institute, we help men recover from their old, tired and depressed selves through safe and effective testosterone replacement therapy. We deliver this therapy after accurate measurements of testosterone levels to ensure that we give testosterone only to the right people. If you have symptoms of low-T or suspect that your levels could be low, speak to one of our urologists. We will ensure to get you back to a more energetic, motivated and happy self. For more information on the diagnosis and treatment for low testosterone, visit the “Advanced Urology Institute” site.
2 Common Types of Incontinence
Urinary incontinence, defined as involuntary and accidental leakage or loss of urine because of defective bladder control, is a common problem in the United States that affects an estimated 25-33 percent of the population. While both men and women can have the condition, more women are at risk of having urinary incontinence because of several factors unique to women. For instance, due to pregnancy, childbirth, different anatomical characteristics in the pelvic region, atrophy (shrinking) of sphincter muscles and menopause, women suffer from urinary incontinence much earlier and more frequently than men do. Urinary incontinence is not a normal consequence of aging, though its prevalence increases with age.
Repercussions beyond Health
Urinary incontinence is not only a health problem, but also poses a variety of psychological, social and emotional difficulties. For instance, women with urinary incontinence may want to avoid certain situations or places for fear of an embarrassing accidental leak. A strong and sudden urge to urinate may cause embarrassment and discomfort, particularly when you are not near a bathroom or toilet. Women also may withdraw from activities they love doing due to the risk of an accidental leak. As a result, urinary incontinence can limit a woman’s activities, diminish her self-confidence and reduce her joy in life. But urinary incontinence is a treatable condition as long as the underlying cause can be identified and addressed.
Two Major Types of Urinary Incontinence
There are two main types of urinary incontinence: stress incontinence and urge incontinence.
1. Stress Incontinence
Stress incontinence is the accidental loss of urine from the bladder due to weak pelvic muscles. Urine loss occurs during physical activity such as when sneezing, laughing, coughing, exercising or doing an activity that exerts pressure on the pelvic muscles. When you are active, you put pressure on the bladder, which in turn allows urine to escape because the pelvic muscles are weak. Stress incontinence often occurs after pregnancy or childbirth because the pelvic muscles have been stretched and weakened and nerves to the bladder may have been damaged. Obesity or excess weight also can put pressure on the weak pelvic muscles and cause stress incontinence.
2. Urge incontinence
Urge incontinence (known as overactive bladder or OAB) is the sudden, intense and uncontrollable urge to urinate, which occurs when the coordination between the brain and bladder is out of sync. For instance, the brain may send voiding signals to the bladder without warning, or pelvic muscles may become too active and contract frequently even before the bladder is full, resulting in feelings of extreme frequency and urgency. Overactive bladder is the term used to describe any incontinence characterized by uncontrollable urgency, frequency, nocturia and dysuria. Urge incontinence is common in women with an inability to control detrusor contractions, but also may occur in women in menopause (due to inadequate estrogen) or with chronic or acute urinary tract infections, bladder stones, bladder cancer, stroke and multiple sclerosis (due to interference with nerve signals responsible for bladder control).
Sign of Something More Serious
There are many reasons why women may leak urine, from serious neurological conditions like multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease and stroke, traumatic injury of the spinal cord, cardiovascular conditions affecting associated nerves, diuretic medicines, diabetes and obesity, alcohol consumption or recurrent urinary tract infections to inflammation that damages bladder nerves or irritates the bladder. It is therefore advisable to seek medical help as soon as you experience any sign of incontinence. Prompt and timely diagnosis and treatment may uncover a serious underlying problem early. At Advanced Urology Institute, we obtain a full history, conduct a comprehensive physical examination, perform specialized testing and treat urinary incontinence as safely and successfully as possible, making sure to deal effectively with all underlying issues.
A Wide Range of Treatment Options
Treatment of urinary incontinence at AUI depends on the type of incontinence and severity of symptoms. Options may include rehabilitation of pelvic muscles using weighted vaginal cones, electrical stimulation or Kegel’s exercises, sacral nerve neuromodulation, biofeedback and bladder retraining, extracorporeal magnetic innervation, occlusive devices (such as vaginal pessaries or urethral plugs), medications (such as Extended-Release Oxybutynin Chloride like Ditropan XL, tolterodine like Detrol, alpha-adrenergic drugs and estrogens), periurethral injection, and minimally invasive surgery. If you have any symptoms, you should see a urologist as quickly as possible to undergo testing, determine the underlying cause and detect any serious problem you may have.
At Advanced Urology Institute, your health is our foremost priority. We provide the right diagnosis and treatment of urinary incontinence that can quickly restore your confidence and enable you to get out there and do the things you love without worrying about accidental leakages. Do not suffer in silence. For more information on urinary incontinence, visit the “Advanced Urology Institute” site.
Treating Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among American men. In fact, it is the most frequently diagnosed non-skin cancer in men, with over 2 million American men currently living with the cancer. Statistically, a new case arises every 3 minutes, one in six American men has prostate cancer, while an American man dies of it every 19 minutes.
Making treatment decisions
At Advanced Urology Institute, we make every effort to deliver world-class treatment and care for patients with prostate cancer. After a diagnosis, our physicians review various treatment options before picking any treatment for the patient. We also conduct further studies, such as biomarker testing and imaging studies, to ensure that we have correctly established the stage or extent of the disease. We use this information to make the right decisions and give prostate cancer patients the most effective treatments. We choose treatment options depending on the cancer itself (high-risk, intermediate risk or low-risk) and patient factors (personal preferences, age and other health issues).
Prostate cancer treatment options
Advanced Urology Institute offers a wide range of innovative and effective diagnostic and treatment procedures for patients with prostate cancer. At the institute, newly diagnosed patients get the opportunity to meet and discuss their condition with renowned and experienced specialists on the same day.
Our treatment options include:
- Active surveillance: For a low-risk prostate cancer that may not harm a patient over the course of his lifetime, urologists at AUI usually recommend close observation. It often comes with secondary chemoprevention.
- Prostatectomy: Prostatectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the prostate. For localized prostate cancer, radical prostatectomy may be employed. However, at Advanced Urology Institute, we commonly apply the robot-assisted technique, which is a minimally-invasive, laparoscopic procedure.
- Radiation: An external beam of radiation is directed at the prostate in order to kill cancerous cells.
- Cryotherapy: Probes are inserted into the prostate gland to allow for the introduction of liquid nitrogen into the gland. Once administered, liquid nitrogen produces an ice ball inside the prostate which destroys cancerous cells.
- Brachytherapy: A radioactive seed is implanted in the prostate. The procedure involves inserting and removing the needles that are used to place radioactive seeds inside the prostate.
- Hormone therapy: Various medications can be administered to reduce or inhibit the secretion of testosterone hormone. Diminished quantities of testosterone means reduced or no growth of the cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Certain drugs may be used to boost the effectiveness of the other treatments, both for metastatic and localized disease.
Multi-disciplinary treatment and care
At Advanced Urology Institute, our goal is to cure prostate cancer while also maximizing the quality of life of our patients. We carefully weigh the benefits of every treatment option against the side effects and develop the most practical individualized treatment programs for all patients. We also believe that effective management of prostate cancer needs extensive collaboration. We have implemented a multidisciplinary approach to treatment that allows our various specialists, such as urologists, radiation oncologists, medical oncologists, radiologists, pathologists and clinical trial nurses to deliberate and get diverse, specialized perspectives before making treatment decisions for any patient. During AUI conferences, detailed discussions among experts help to clarify the benefits and risks of various diagnostic tests and treatment options, resulting in better treatment outcomes for our patients.
Advanced Urology Institute uses image-guided targeting, MRI, ultrasound and fusing 3-D guidance to boost the accuracy and usefulness of prostate biopsies. We also apply minimally-invasive, outpatient procedures in most cases. So, with our comprehensive consultation service and multidisciplinary approach that incorporates the latest technologies, research developments and expertise, all our patients can be sure of the best possible prostate cancer treatment. Want help with prostate cancer? Get more information from our “Advanced Urology Institute” site.